
Alex Sikorski
Jun 26, 2022
Watering Plants (LeetCode #2079)
#leetcode medium
#leetcode
#java
The problem starts by noting where you can refill your watering can:
You want to water n plants in your garden with a watering can. The plants are arranged in a row and are labeled from 0 to n - 1 from left to right where the ith plant is located at x = i. There is a river at x = -1 that you can refill your watering can at.
Each plant needs a specific amount of water. You will water the plants in the following way:
- Water the plants in order from left to right.
- After watering the current plant, if you do not have enough water to completely water the next plant, return to the river to fully refill the watering can.
- You cannot refill the watering can early.
You are initially at the river (i.e., x = -1). It takes one step to move one unit on the x-axis.
Given a 0-indexed integer array plants of n integers, where plants[i] is the amount of water the ith plant needs, and an integer capacity representing the watering can capacity, return the number of steps needed to water all the plants.
Example 1:
Input: plants = [2,2,3,3], capacity = 5
Output: 14
Explanation: Start at the river with a full watering can:
- Walk to plant 0 (1 step) and water it. Watering can has 3 units of water.
- Walk to plant 1 (1 step) and water it. Watering can has 1 unit of water.
- Since you cannot completely water plant 2, walk back to the river to refill (2 steps).
- Walk to plant 2 (3 steps) and water it. Watering can has 2 units of water.
- Since you cannot completely water plant 3, walk back to the river to refill (3 steps).
- Walk to plant 3 (4 steps) and water it.
Steps needed = 1 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 3 + 4 = 14.Example 2:
Input: plants = [1,1,1,4,2,3], capacity = 4
Output: 30
Explanation: Start at the river with a full watering can:
- Water plants 0, 1, and 2 (3 steps). Return to river (3 steps).
- Water plant 3 (4 steps). Return to river (4 steps).
- Water plant 4 (5 steps). Return to river (5 steps).
- Water plant 5 (6 steps).
Steps needed = 3 + 3 + 4 + 4 + 5 + 5 + 6 = 30.Example 3:
Input: plants = [7,7,7,7,7,7,7], capacity = 8
Output: 49
Explanation: You have to refill before watering each plant.
Steps needed = 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 + 3 + 3 + 4 + 4 + 5 + 5 + 6 + 6 + 7 = 49.
Initial Thoughts
It is immediately apparent to me that this can be done within one loop, iterating back to count steps is not necessary and will be time-consuming. The reason why is that we know the position of the plant in the plants array and can use the index to calculate steps.
So how do we know when to refill? We simply check if the plant will require more water, e.g. if(can - plants[i] < 0), if this value is below zero we will have to refill, add our steps and calculate the new value of can before moving on to the next plant.
Otherwise, the status of can would be at or above zero meaning we can continue without refilling, so we would add one step and calculate a new capacity of our can by subtracting the water required by the plant i.e. plants[i].
Solution
class Solution {
public int wateringPlants(int[] plants, int capacity) {
int steps = 0;
int can = capacity;
for(int i = 0; i < plants.length; i++){
if(can - plants[i] < 0){
// check if needs refill
steps += (i * 2);
// add steps for going back and forth
can = capacity;
// refill can then later use water needed
// this works because of constraints:
// capacity >= max(needed water)
}
can -= plants[i];
// use water needed
steps += 1;
}
return steps;
}
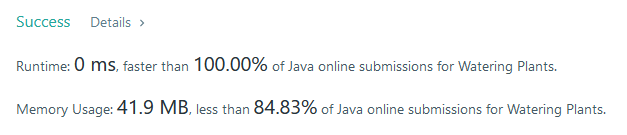
}Result

Alex Sikorski
Currently working as a full stack Software Engineer and curiously seeking new knowledge in free time.